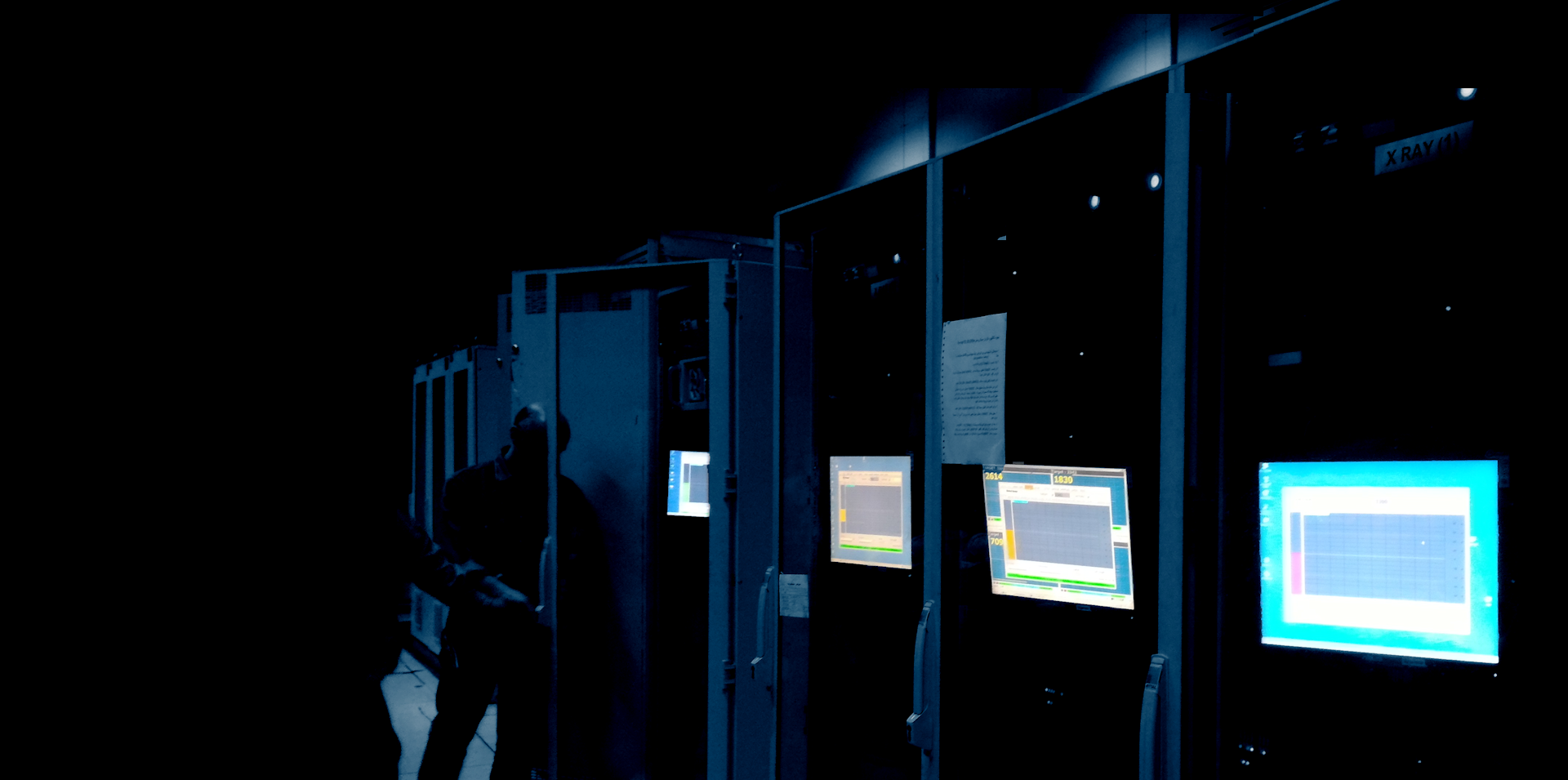
Online shape and measurement for coupling gears
In modern manufacturing and quality control processes, the surface finish of mechanical parts plays a critical role in product performance, durability, and functionality. Whether in the aerospace, automotive, medical, or tooling industries, precise surface texture measurements are essential. One of the most reliable instruments for this purpose is the profilometer.
A profilometer is a measuring instrument used to evaluate the surface roughness and topography of a material. It captures the fine details of a surface profile, typically in the micron or nanometer range. Profilometers can be contact-based or non-contact:
Surface texture affects how parts interact, especially in applications involving friction, lubrication, sealing, or wear. For example:
- In engines, smoother surfaces reduce friction and wear.
- In sealing surfaces, proper roughness ensures effective sealing without leakage.
- In optical components, surface smoothness impacts light reflection and performance.
Profilometers help ensure that components meet the surface roughness tolerances specified in engineering drawings (e.g., Ra, Rz, Rq).
Profilometers measure a wide range of surface parameters. The most commonly used include:
- Ra (Roughness Average): The arithmetic average of absolute deviations from the mean line.
- Rz (Average Maximum Height): The average of the highest peak to lowest valley in each sampling length.
- Rq (Root Mean Square Roughness): Similar to Ra but uses the root mean square value of profile deviations.
- Rt (Total Height): The vertical distance between the deepest valley and the highest peak in the evaluation length.
1. Measurement Process
- A scan is performed using reflected light
- Captures the surface profile and calculates dimensions and roughness parameters.
2. Data Analysis
- The profilometer software generates a surface profile graph and a report with dimensions and roughness values.
- Results are compared against tolerances specified in the design requirements.
- Measurements can be saved, exported, and used for traceability or reporting.
3. Interpretation and Action
- If values are within tolerance: part is approved.
- If out of tolerance: rework or reject the part, investigate machining or tooling issues.
Profilometers are widely used in:
- CNC machining and grinding for surface finish validation.
- Injection molding and die casting to evaluate mold surface quality.
Advantages:
- High precision and repeatability.
- Ability to measure complex surface geometries.
- Non-destructive testing.
- Compliance with international surface texture standards.