Remote Monitoring using a Tablet and Laptop
| In today’s digitally connected world, remote monitoring of industrial and commercial machinery has become increasingly critical for maintaining productivity, reducing downtime, and improving operational efficiency. Leveraging mobile and portable devices such as tablets and laptops enables technicians, engineers, and management to monitor machine performance in real-time, regardless of their location. This article explores the key components, benefits, and considerations involved in remote machine monitoring using tablets and laptops. |  |
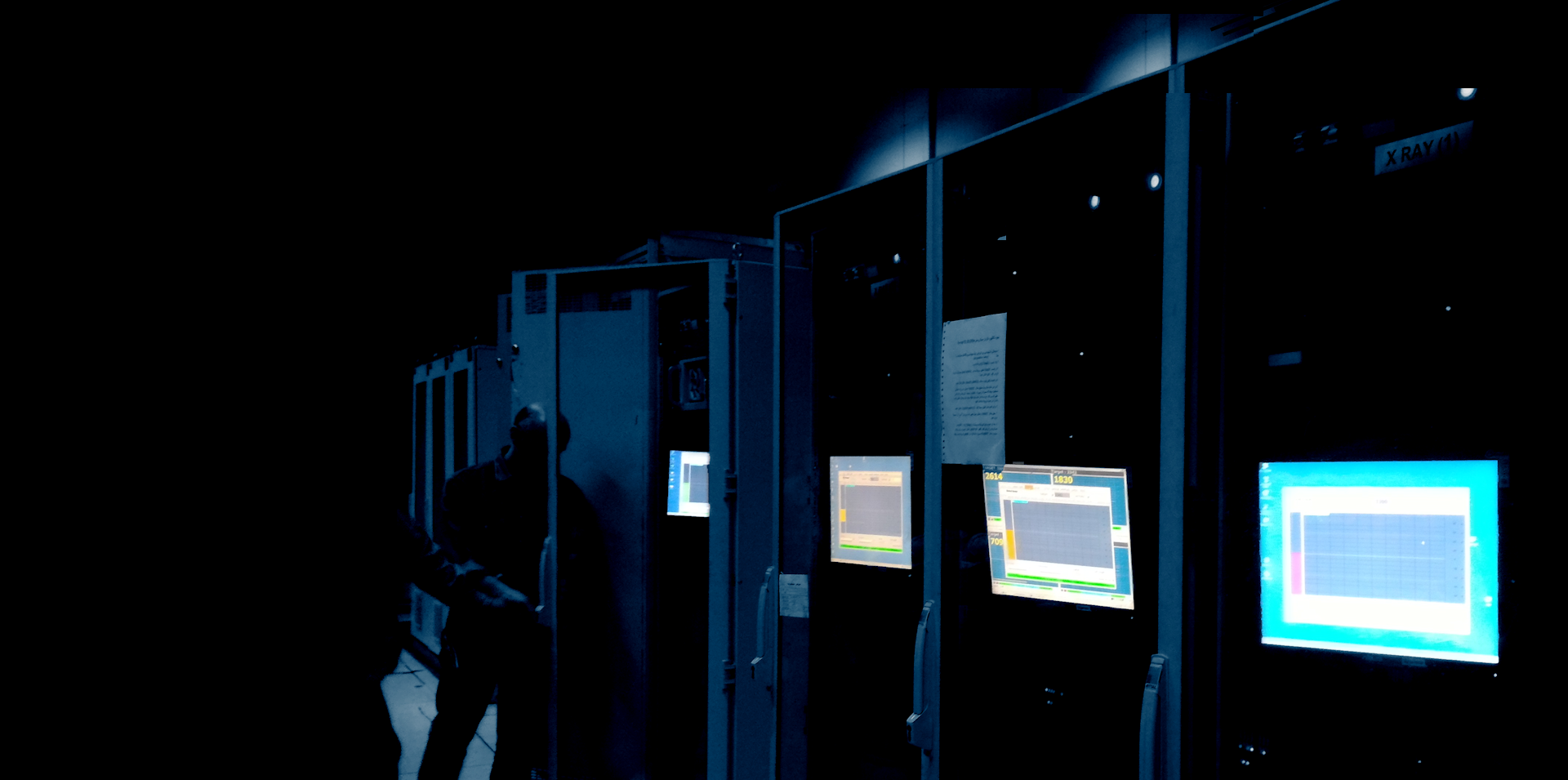
Remote machine monitoring involves collecting and analyzing operational data from a machine or system without being physically present. Sensors installed on the machine collect data, which is then transmitted through a network to an interface that can be accessed on a remote device such as a laptop or tablet.
This capability allows for:
- Real-time diagnostics
- Performance analysis
- Predictive maintenance
- Remote troubleshooting
- Efficient resource management
To enable remote monitoring via a tablet or laptop, several components must be integrated:
Sensors and Data Acquisition
The machine must be equipped with appropriate sensors to capture relevant data such as temperature, vibration, pressure, speed, and power usage. These sensors form the basis of real-time monitoring.
Control System (PLC or Embedded Controller)
The sensors send data to a programmable logic controller (PLC) or embedded system that processes the inputs and transmits them through a communication protocol such as MQTT, Modbus, or OPC UA.
Communication Network
The system needs a reliable method to transmit data to remote devices. This can be via Ethernet, Wi-Fi, cellular (4G/5G), or even satellite in remote areas.
Cloud-Based or Local Monitoring Software
A central part of remote monitoring is the software interface—either cloud-based platforms or locally hosted web dashboards. These interfaces visualize real-time data and allow for control functions, alerts, and historical analysis.
Tablet or Laptop Interface
The tablet or laptop acts as the user interface, allowing remote access to machine data. These devices use web browsers or dedicated apps to connect to the monitoring platform.
- Portability and Flexibility
Tablets provide a highly portable option for technicians on the move, while laptops offer more processing power for detailed diagnostics and data analysis.
- Real-Time Access
Users can access machine status and performance metrics in real-time, enabling quicker decision-making and faster response to anomalies.
- Multi-Platform Support
Most modern remote monitoring platforms are web-based or offer cross-platform apps, allowing seamless switching between devices based on user preference or environment.
- Remote Troubleshooting
Remote access can eliminate the need for on-site visits for routine inspections, enabling experts to troubleshoot issues from anywhere.
- Improved Safety
Remote monitoring reduces the need for physical presence in hazardous or hard-to-reach environments, improving operator safety.
Remote monitoring of machines using tablets and laptops offers a powerful combination of mobility, flexibility, and data-driven decision-making. By leveraging the right hardware, software, and connectivity infrastructure, businesses can improve operational efficiency, reduce maintenance costs, and ensure greater uptime. As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to evolve, remote monitoring is set to become an integral part of smart manufacturing and industrial automation strategies.